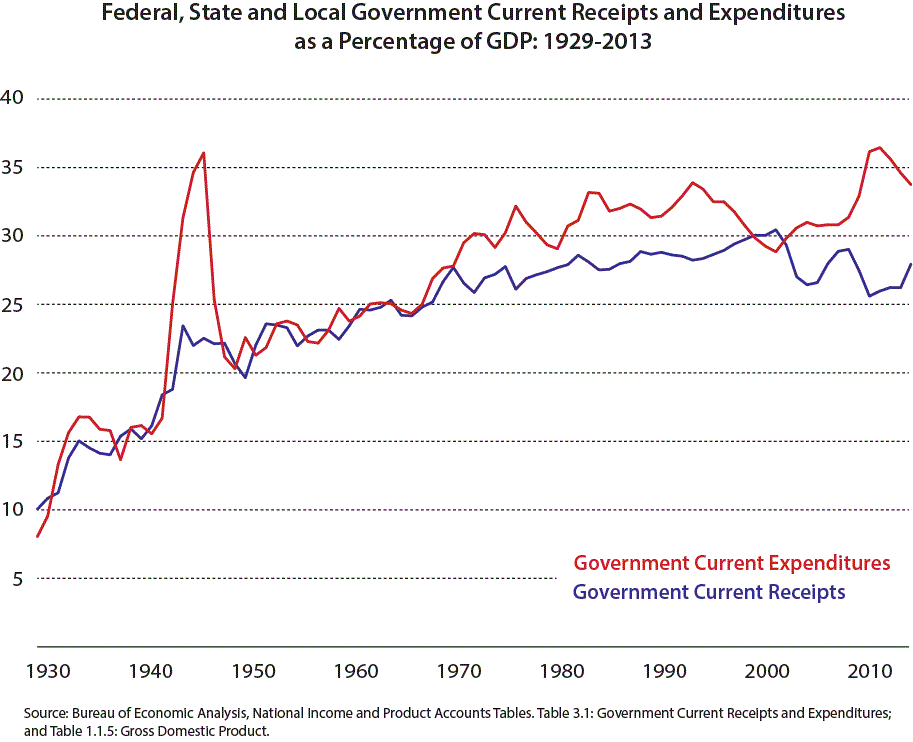
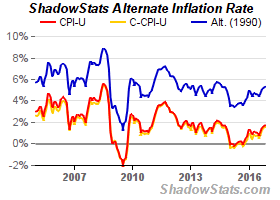
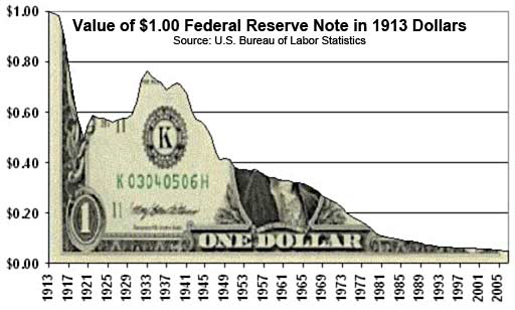
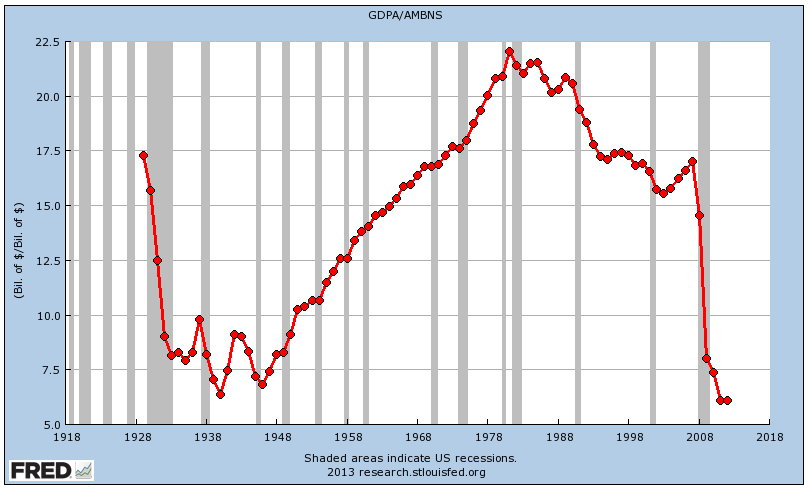
Mr. Oshima is a true Zen martial arts master, 25 years ago I was fortunate to be in a Karate warmup and he asked the class "How do you recognize the truth?". People responded with... "logic", "reasoning", "evidence" etc. and he summarized what he heard with the word "experience". Here's my experience and takeaways about the challenges of figuring out what's true.
Besides martial arts instructors, I submit that scientists, philosophers and lawyers have studied truth the most. Here's a dive into how they think about it.
 Science and Mathematics:
Science and Mathematics:
From Francis Bacon to Karl Popper and Thomas Kuhn
What constitutes truth in science evolved from inductivism, attributed to Francis Bacon in the 1600's, where the scientific method is traversed and "laws" are added and subtracted based on the "best" experimental observations...
...to Karl Popper who (in the 1900's) created a more rigorous, "falsification" doctrine where predicting the future (especially improbable futures) are experimentally confirmed or falsified. This became the gold standard for scientific laws especially in Physics.
Falsification was overlayed with Thomas Kuhn's 1962 "The Structure of Scientific Revolutions" observation that science did not evolve linearly but had "paradigm shifts" in understanding that create a new foundation to rebuild the laws around ( quantum mechanics comes to mind ). A cyclical structure outside of traversing the Scientific Method.

Whitehead and Russell's attempt to prove that Mathematics could be the foundation of absolute truth for mankind ... until Kurt Godel
Alfred North Whitehead and Bertrand Russell from 1910-1913 attempted to prove that Mathematics could be the foundation of absolute truth for mankind ... until Kurt Godel proved that despite it's rigor, even mathematical proofs were incomplete, and how we think hard-wires limits to our understanding.
I have created an order of increasing "Rigor" in Science that is based upon observational sample sizes and a lifetime of reading scientific literature.
- Mathematics
- Physics and Engineering
- Biological Sciences
- Non-biological Psychology, Social Sciences and Humanities
Key Idea 1: Standards of truth in Science have evolved and using the "Scientific Method" still creates different levels of confidence in scientific conclusions...not all "Science" is created equal!
Law:
Legal Standards of proof in the U.S. justice system
- A Preponderance of Evidence (greater than a 50% chance the proposition is true)
- Clear and Convincing (clear,unequivocal, satisfactory and convincing evidence making it more probably true than not)
- Beyond a reasonable Doubt (no plausible reason to believe otherwise)
Theories of the Past are always "A preponderance of Evidence" argument. They are falsifiable only if the theory can predict the future (accurately). Predicting the future with statistical significance, makes it "Clear and Convincing". The farther back a "theory of the past" attempts to describe the least observable it is (without a time machine). Therefore it becomes a game of piling on evidence. This causes the admissibility of evidence to become the most critical element in supporting the theory!
This explains why the theory of evolution and theory of anthropomorphic climate change can be controversial even among well educated experts in these fields. Since these "theories of the past" are based upon a "preponderance of evidence", the best way to defend a theory is to restrict what is "admissible" evidence. Can evolutionary scientists predict the next species or dominant gene to emerge? Will climate scientists reveal what their 20 year old model predicted for 5 years ago and today? Even very smart people thought the world was flat and Newtonian mechanics was accurate. Here's an article that describes high profile cases where accurate future predictions were made, but the scientific theory behind them we now believe was wrong!
Key Idea 2: "Preponderance of evidence" arguments in science or law create incentives to bias admissibility of evidence!
Main Stream Media , Internet Sites and Motivations
Fairness Doctrine and Equal Time Rule
From 1949-1987 the FCC required holders of broadcast licenses (e.g. ABC, CBS and NBC) to:
- Present controversial issues of public importance
- Report the issues in an "honest, equitable and balanced manner"

Everybody trusted Walter... active from 1935-2009 "In seeking truth you have to get both sides of a story"
This Fairness Doctrine policy was upheld in the supreme court in 1969, reasoned by the scarceness of the broadcast spectrum.
The Equal Time Rule originally enacted in 1927 requires broadcast stations to provide political candidates equivalent opportunity (at the same price) if requested.
Because today's MSM and Internet sites are not subject to a "journalistic law" (or regulatory requirement) such as the Fairness Doctrine, it allows individuals and corporations to leverage the First Amendment and their access/control of modern media outlets to support their personal objectives.
 Publication Bias: Suppose I flip coins and publish results for a living. If the peer reviewed "Journal of Classical and Quantum Coin Flipping" only accepts my articles when results come up heads (just as my research grant proposal "coins are political" had speculated) and the NYTimes reports "Scientists agree that coins are politically biased". Is this fake news? Did the news accurately report bad science? Was the science bad because of distorted financial incentives or overly stated conclusions? Or did motivational self-interests of the publication bias the outcome? Of course all of these things happen in the real world.
Publication Bias: Suppose I flip coins and publish results for a living. If the peer reviewed "Journal of Classical and Quantum Coin Flipping" only accepts my articles when results come up heads (just as my research grant proposal "coins are political" had speculated) and the NYTimes reports "Scientists agree that coins are politically biased". Is this fake news? Did the news accurately report bad science? Was the science bad because of distorted financial incentives or overly stated conclusions? Or did motivational self-interests of the publication bias the outcome? Of course all of these things happen in the real world.
Key Idea 3: Societal issues pressure (financial, ideological, political) information sources to bias evidence while legislative protections have decreased. Different incentives are usually not tied to pure truth.
Why the Public is Easily Duped
“Is the pope Catholic? " a yes answer is plausible, possible, feasible and probable. “Is a Catholic the pope?" The answer is probably not although it might be plausible, possible and feasible that a given catholic is the pope. If you change the order, a statement doesn’t survive.”
The public (and even good scientists and engineers) are often fooled by things that are plausible and possible because judging feasibility and probability takes MUCH MORE EXPERTISE/WORK in the relevant field. This is why a technical scam like Theranos was able to raise $billions and dupe many high-profile people to join their board.
Something Plausible may not be Possible...
...the Possible may not be Feasible...
...the Feasible may not be Probable.
The Farnam Street Blog (a favorite site of mine) published a great article
Deductive vs Inductive Reasoning: Make Smarter Arguments, Better Decisions, and Stronger Conclusions
They identify several types of evidence used as reasoning by people to point to a truth:
- Direct or experimental evidence — This relies on observations and experiments, which should be repeatable with consistent results.
- Anecdotal or circumstantial evidence — Over-reliance on anecdotal evidence can be a logical fallacy because it is based on the assumption that two coexisting factors are linked even though alternative explanations have not been explored. The main use of anecdotal evidence is for forming hypotheses which can then be tested with experimental evidence.
- Argumentative evidence — We sometimes draw conclusions based on facts. However, this evidence is unreliable when the facts are not directly testing a hypothesis. For example, seeing a light in the sky and concluding that it is an alien aircraft would be argumentative evidence.
- Testimonial evidence — When an individual presents an opinion, it is testimonial evidence. Once again, this is unreliable, as people may be biased and there may not be any direct evidence to support their testimony.
Key Idea 4: Evidence can be evaluated with increasing confidence by testing whether it is a) plausible b) possible c) feasible d) probable with each step depending upon the previous and requiring more rigor.
Truth Takeaways:
1- Focus on confidence in conclusions based upon evidence, not whether A or B right
2- The following evidence is called "Science" in the media but "Scientific proof" varies tremendously across disciplines, so weight evidence differently
Opinionated evidence (low) -Testimonials, circumstantial, argumentative
Experimental (medium) - "study" experiments
Future predictions (high) -experiments that support/oppose a future prediction
3- Evaluate a statement from plausible --> possible --> feasible --> probable with increasing diligence, if you cannot do the diligence, then settle for "I don't know"
4- Practice delivering counter-arguments with equivalent nuance as your position to guard against confirmation bias and fear of being wrong
5- Accept that in some areas (especially human behavior) truth is subjective e.g. Ethicists believe right and wrong standards change over time and across the world
6- Remember that MOST OF THE TIME you're not sure!